Classification of images of cats and dogs is a common task in the field of computer vision. In this blog post, we will walk through the process of building a classifier using Keras and Python3 that can accurately distinguish between images of cats and dogs.
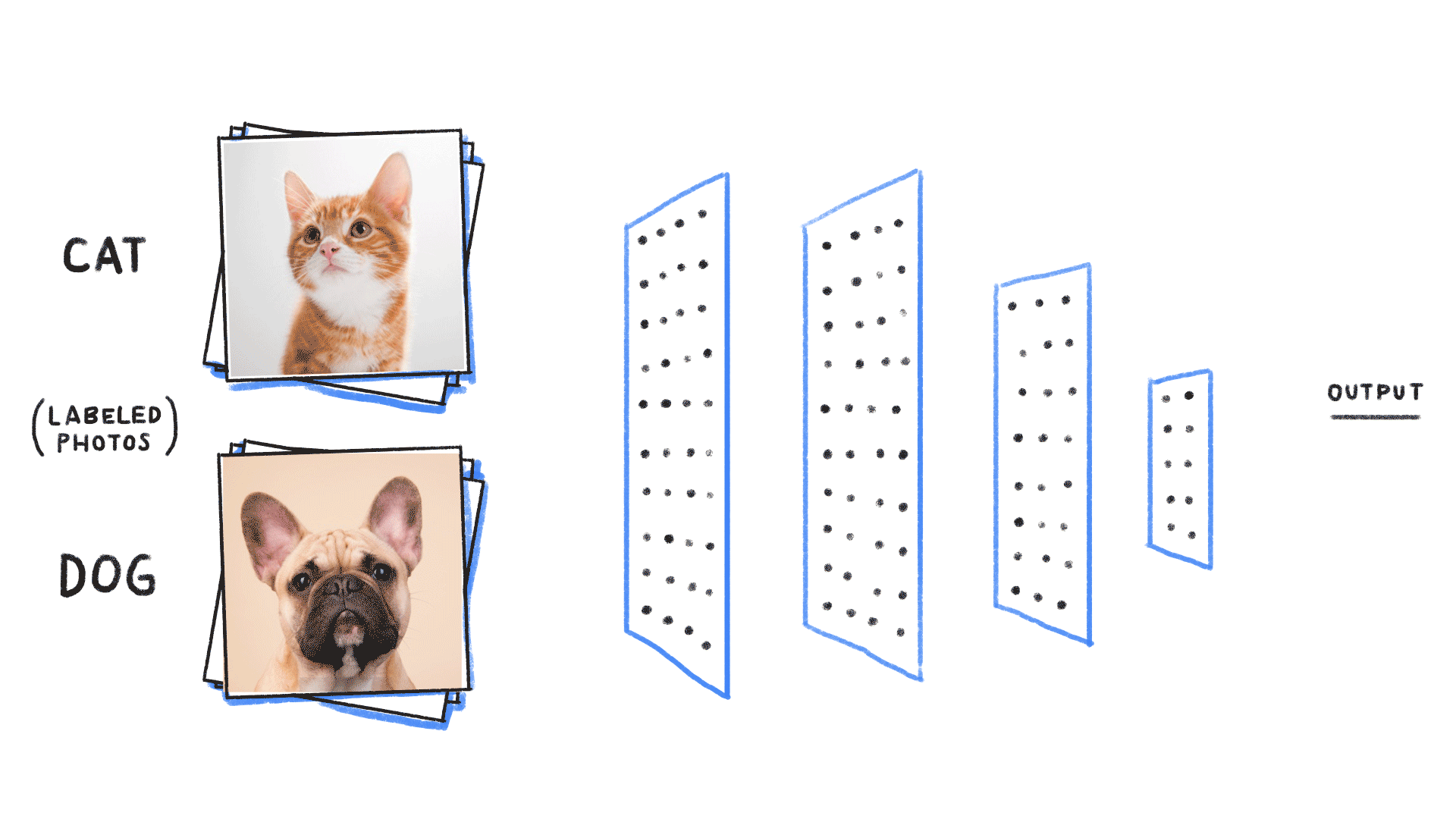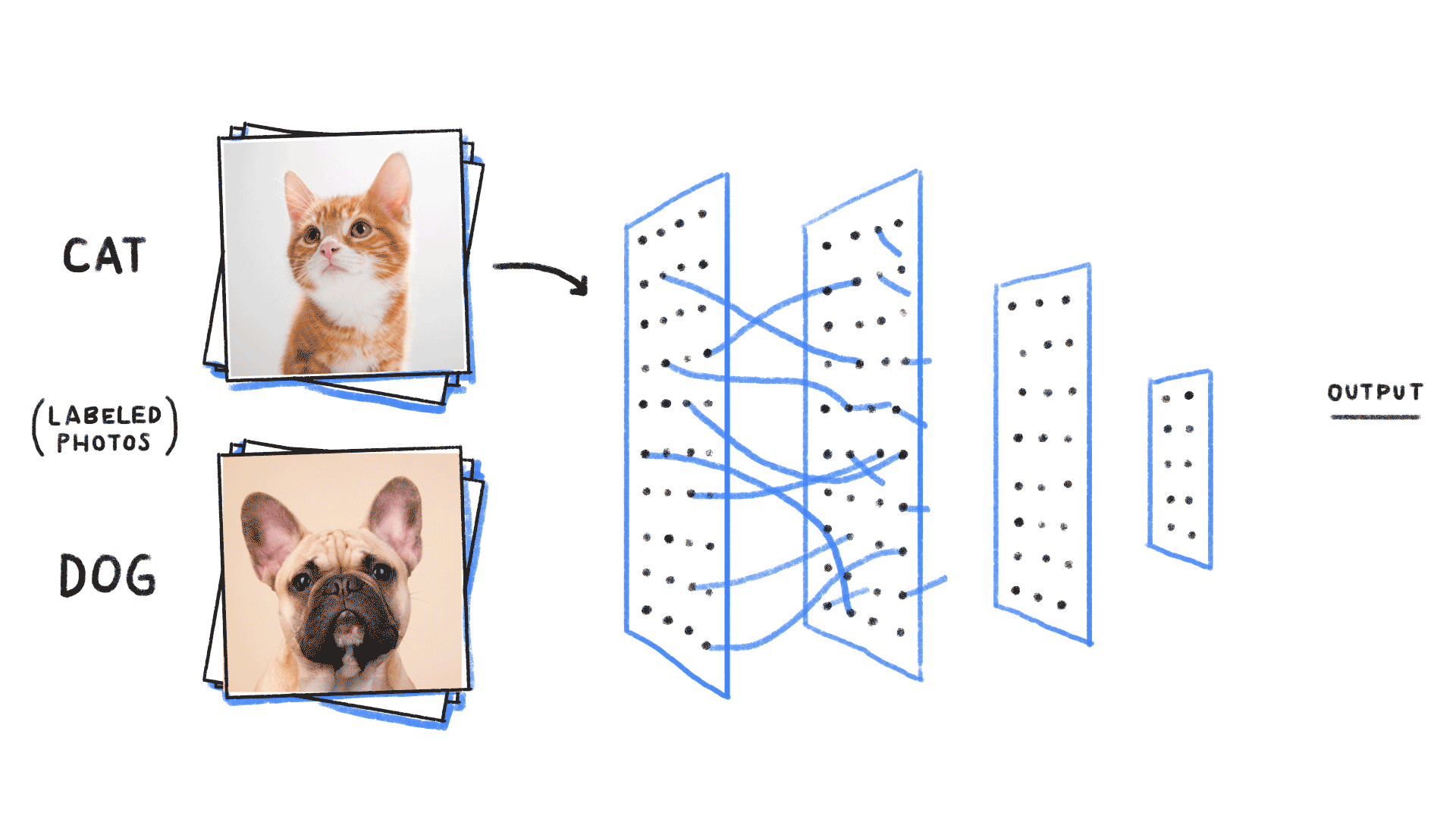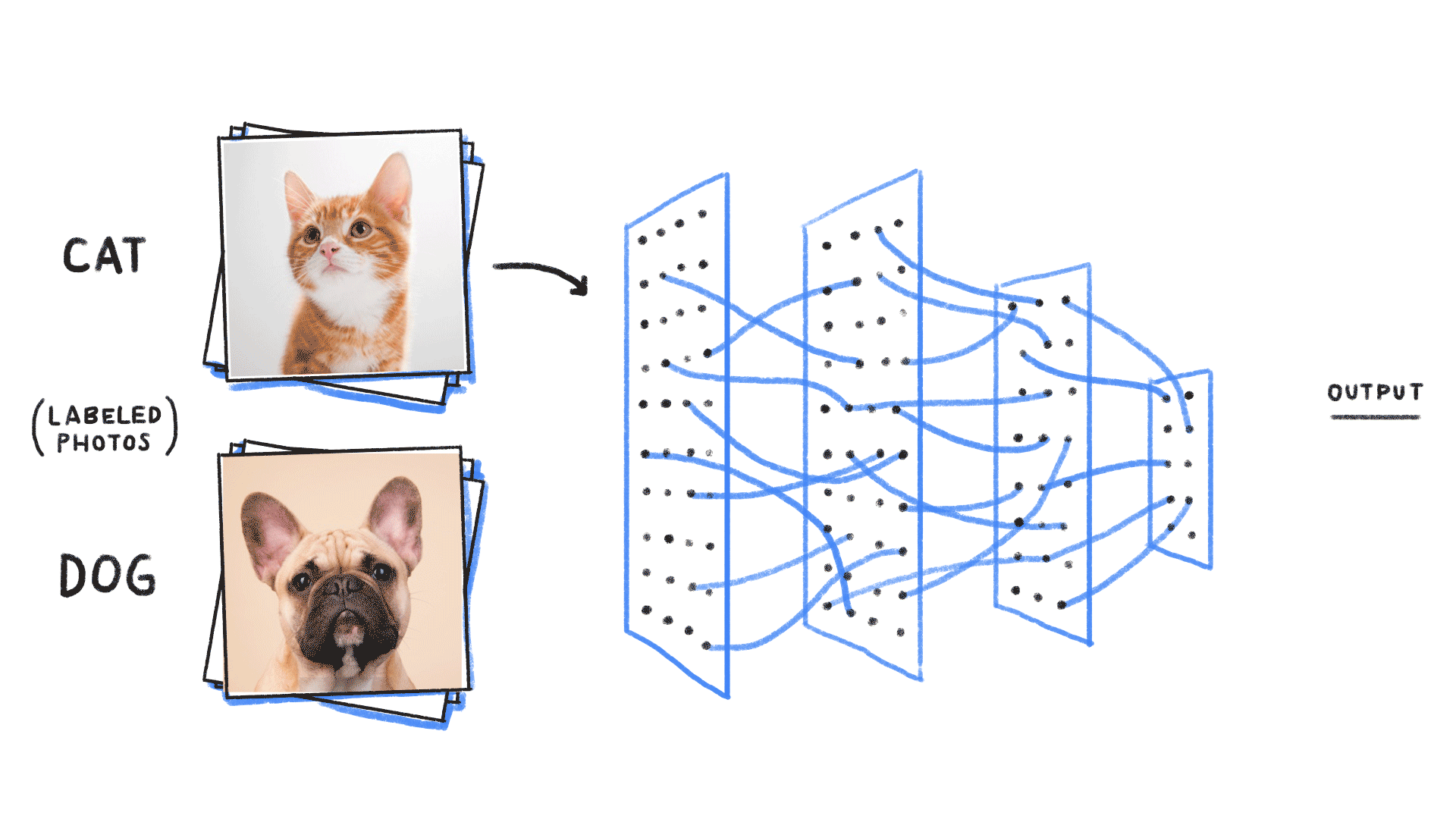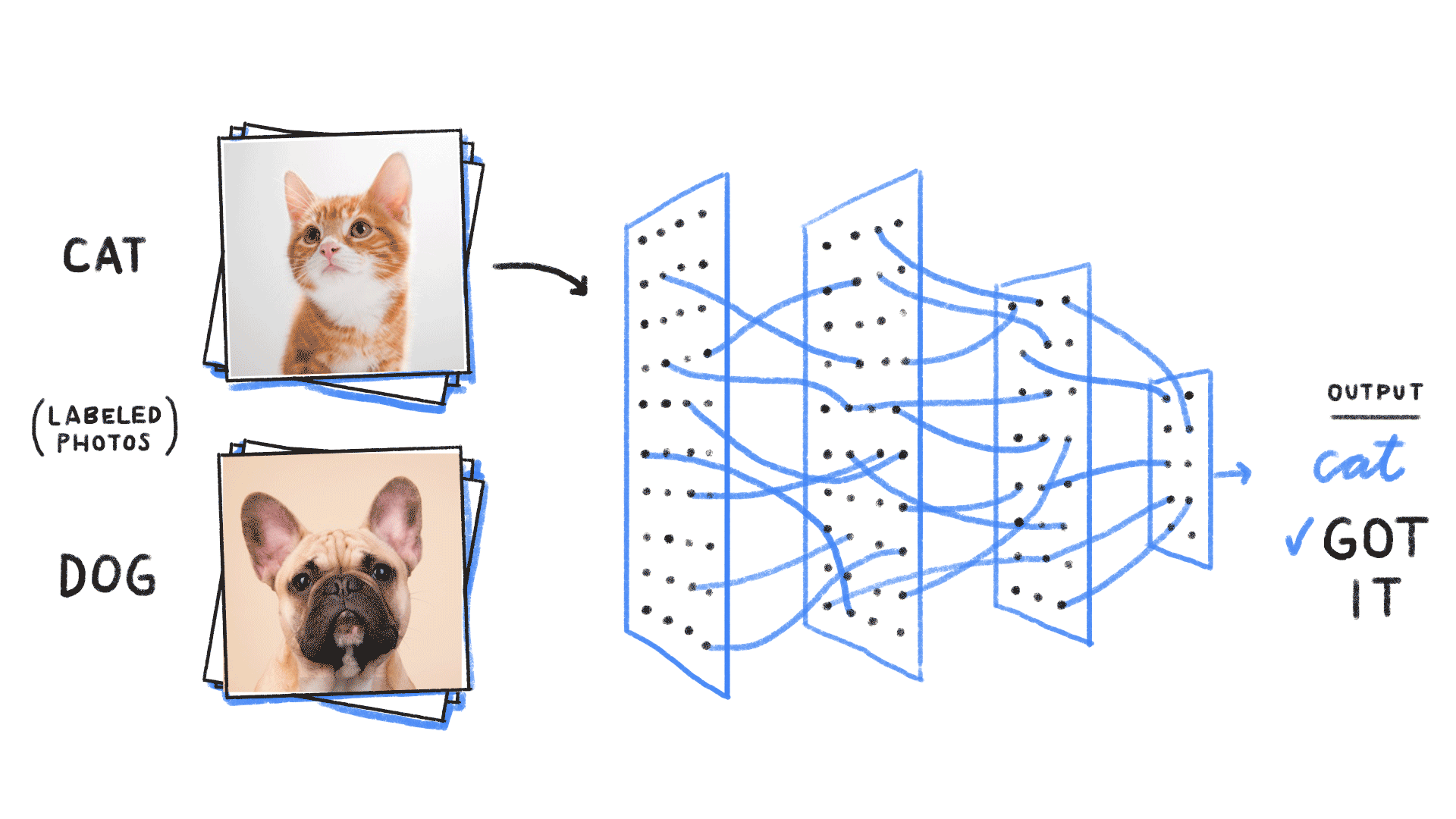
Image-source- https://github.com/ReiCHU31/Cat-Dog-Classification-Flask-App
Numpy: for working with arrays and matrices
Matplotlib: for visualizing data
TensorFlow: for building and training the model
Keras: for building the neural network layers
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras import models
Next, we will need to obtain a dataset of images of cats and dogs. There are many publicly available datasets that can be used for this task, such as the Kaggle Cats and Dogs dataset. Once we have obtained the dataset, we will need to preprocess the images by resizing and normalizing them. We will also need to divide the data into training and test sets.
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# Set the image size
IMAGE_SIZE = (150, 150)
# Create the training and test data generators
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale = 1./255)
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale = 1./255)
# Create the training and test generators
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
'data/train',
target_size = IMAGE_SIZE,
batch_size = 32,
class_mode = 'binary')
test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
'data/test',
target_size = IMAGE_SIZE,
batch_size = 32,
class_mode = 'binary')
Once the data is preprocessed, we can build the neural network model using Keras. We will use a simple convolutional neural network (CNN) with two convolutional layers and two fully connected layers.
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(150, 150, 3)))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(512, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
Once the model is defined, we can then compile and train it using the training data.
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['acc'])
history = model.fit(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=100,
epochs=10,
validation_data=test_generator,
validation_steps=50)
Now that the model is trained, we can evaluate its performance on the test data using the evaluate() function.
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_generator, steps=50)
print('Test accuracy:', test_acc)
Finally, we can use the trained model to make predictions on new images.
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
# Load an image file
img = image.load_img('data/test/dogs/dog1.jpg', target_size=(150, 150))
# Convert the image to a numpy array
x = image.img_to_array(img)
# Add an extra dimension to the array (required by the model)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
# Make a prediction
predictions = model.predict(x)
# Print the prediction
print(predictions)
With this, we have successfully built a classifier that can distinguish between images of cats and dogs using Keras.